
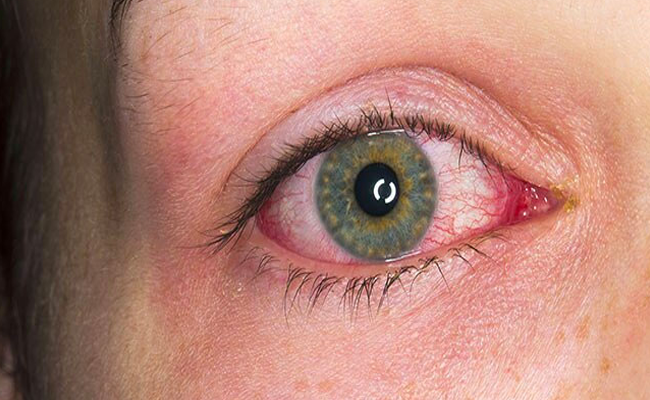
Uveitis management involves a combination of treatments aimed at reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and preserving vision. The treatment approach depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause of uveitis.
Effective management of uveitis often requires close collaboration between ophthalmologists and other specialists, such as rheumatologists, infectious disease specialists, or oncologists, depending on the underlying cause. The goal of treatment is to control inflammation, relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and preserve vision.