
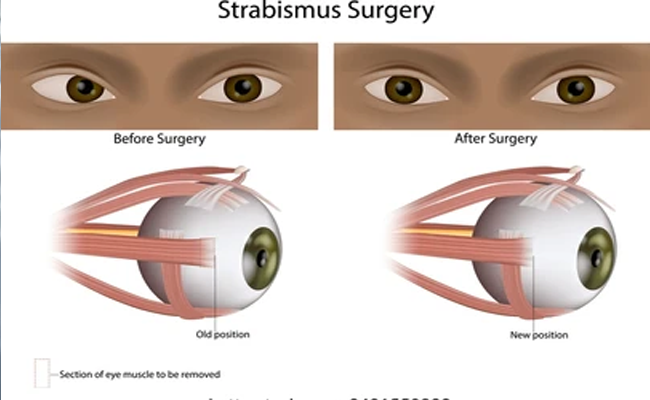
Squint, also known as strabismus or cockeye, refers to a condition where the eyes are misaligned and do not point in the same direction. Squint surgery, also called strabismus surgery, is a procedure performed to realign the eyes and correct the alignment problem.
Squint surgery can have a significant positive impact on both the appearance and function of the eyes, improving visual alignment and quality of life for those affected by strabismus.